What is Frontrunning?
MEV, or maximal extractable value, is a hidden tax on Ethereum transactions that has been responsible for over a billion dollars in value loss for traders to date.
Frontrunning is a particular type of MEV that affects all forms of Ethereum transactions including trades, NFT mints, and more. This article is part of a series on MEV where we also cover the other two common types of MEV: sandwich attacks and backrunning.
What is frontrunning and how does it work?
Frontrunning occurs when a user makes a transaction but gets "front run" by an MEV bot who makes the same transactions ahead of them.
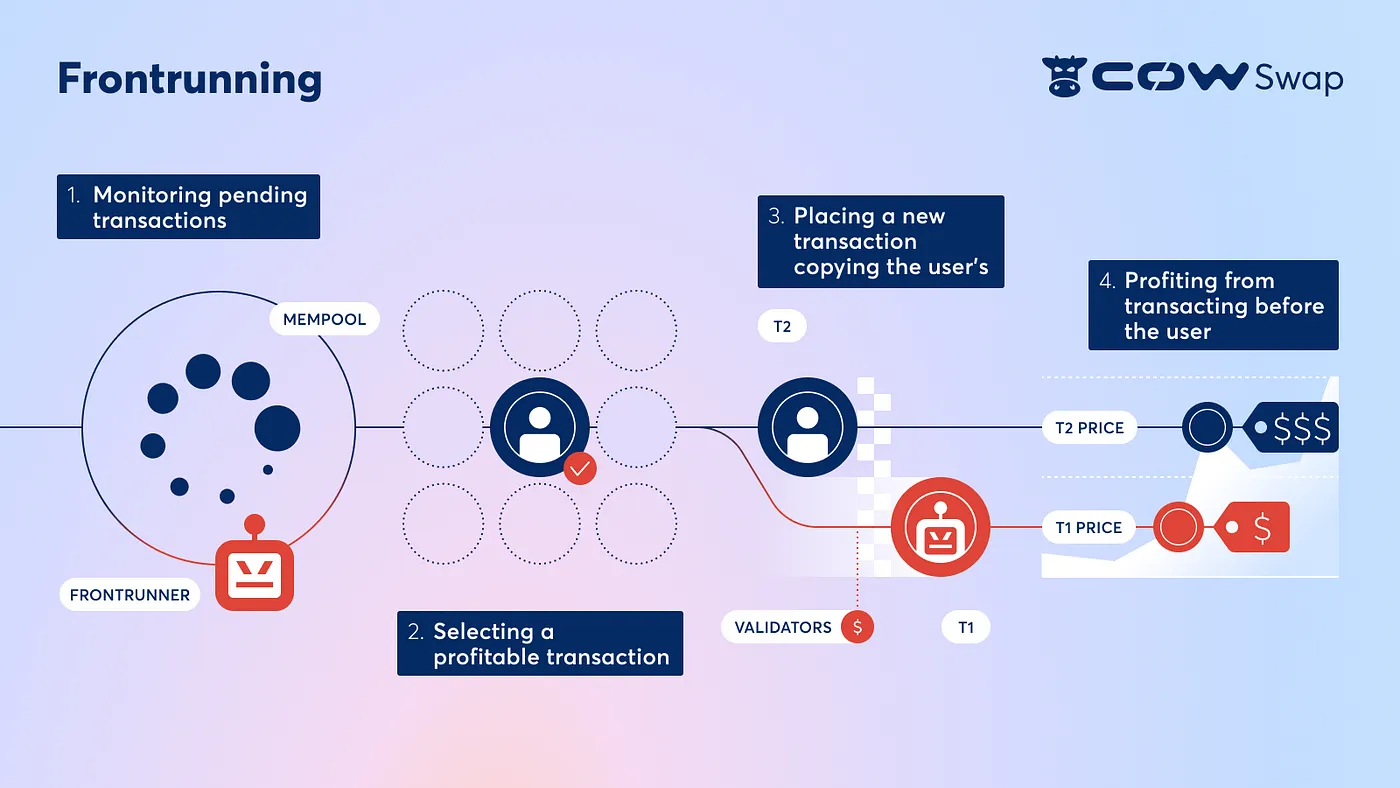
MEV bots monitor pending transactions in the mempool and place their transaction ahead of others, capitalizing on the order of transactions within a block. This approach allows them to gain a significant edge, profiting from traders placing transactions. Frontrunning occurs when an MEV bot monitors the mempool for a trader's pending transaction. Spotting a potential trade, the bot quickly duplicates the users transaction so that they can be the one to get the tokens or the opportunity that the user detected.
The Frontrunning Process
Frontrunning takes advantage of the open nature of the blockchain mempool, as anyone can view transactions. MEV bots exploit this transparency to hijack trades. Here's a basic rundown of the process:
- Monitoring Pending Transactions: The first step involves monitoring the blockchain network's mempool, a holding area for pending transactions. Here, frontrunners, who are often sophisticated bots, scan the mempool to identify transactions that can carry significant value that they want to snatch away or that could influence the price of a particular asset.
- Selecting Profitable Transactions: The frontrunner will analyze the potential market impact once such a transaction is identified. For instance, if a large buy order for a specific token is detected, the frontrunner knows that this transaction could increase the asset's price once processed.
- Placing a New Transaction: The frontrunner will initiate their buy order for the same asset, intending to get their transaction processed before the initially detected transaction. They typically give the validators a higher "tip" to execute their transaction first in the block in comparison to the target transaction.
Example: Frontrunning in DeFi
A notable example of DeFi frontrunning involves the notorious MEV bot named "jaredfromsubway.eth." In one case, a user, 0x3a7822, intended to trade 2 ETH for another token, $BOB.
How the frontrunning attack was executed
This trade was noticed by the bot jaredfromsubway.eth, which monitored the mempool for transactions it could take advantage of.
Once the transaction entered the mempool, Jaredfromsubway.eth quickly executed its own transaction to buy $BOB with ETH, strategically placing it as the first in the block, and knowing that he would get the assets at a discount as the transactions behind will increase the price $BOB. MEV allows validators to prioritize transactions that are of the most value to them. Consequently, the bot's transaction, being the first one in the block, was confirmed ahead of the user's transaction.
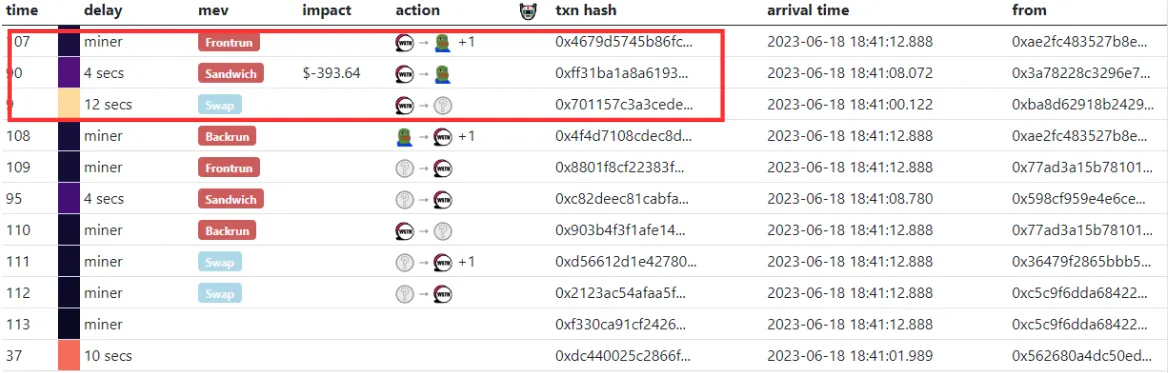
The consequences of the frontrunning attack
The frontrunning attack triggered an increase in the price of $BOB tokens due to the additional demand created before the user's transaction was processed. When the user's original order of 145M $BOB was executed, it was conducted at this now-inflated price, leading to user 0x3a7822 receiving way fewer $BOB tokens, hence losing out on the value they could have otherwise captured.
Jaredfromsubway.eth completed its MEV attack by selling its $BOB tokens at an increased price, resulting in a profit, a second move that made this MEV attack a sandwich attack. In this scenario, the price slippage triggered by the frontrunning bot meant that user 0x3a7822 encountered a worse trade-off, ultimately making a loss while the MEV bot profited - an estimated gain of 0.1 ETH.
An alternative frontrunning scenario
If user, 0x3a7822 identified a liquidation opportunity faster than anyone else and sent its transaction to the mempool to get the discounted assets from the liquidation in the first place, then Jaredfromsubway.eth would have seen this and would have replaced the users transactions with the transaction of its own, but with a higher gas fee, and thus more has an increased likelihood to of being processed faster, and effectively stealing the opportunity of capturing value away from the user.
How Harmful is Frontrunning?
While frontrunning may seem harmless or even clever to some, it can adversely affect individual traders and compromise the overall integrity of the Ethereum network.
Impact on traders
Frontrunning disrupts the fair operation of financial markets. By exploiting pending transactions, frontrunners manipulate market conditions to their benefit. This can lead to distorted prices, impacting regular traders who abide by market rules. What's more, these traders miss out on the value they would have otherwise derived from their trades. But most importantly, frontrunning attacks prevent users from receiving the value of the trading opportunity they identified.
Long-term market consequences
Over time, persistent frontrunning can erode market confidence. As traders realize they are consistently at a disadvantage due to frontrunning, they may lose faith in the integrity of the market and choose to leave. This could result in diminished market participation and liquidity, both of which are critical for overall market health and efficiency.
Network effects
Frontrunning can also have wider implications for the underlying network. It can cause network congestion, since unnecessary transactions in a block slow down transaction processing times.
MEV Blocker takes a firm stance against all forms of Maximal Extractable Value (MEV), including frontrunning, as they are detrimental to traders and the wider Ethereum ecosystem. MEV Blocker was built to cultivate a fair and transparent trading environment that best serves the interests of all market participants.